Generative Engine Optimization Strategies: Complete Beginner’s Guide for SEO & AI Search
Author: Sibtain Haider
Credentials: SEO Strategist & Digital Marketing Consultant
Experience: 3+ years in SEO, content, and growth marketing
Reviewed by: Senior SEO / Marketing Consultant
Introduction: Why Traditional SEO No Longer Tells the Full Story
If your organic traffic feels inconsistent, impressions are rising but clicks are not, or your content ranks yet fails to influence AI-generated answers, you’re not imagining things.
Search behavior is changing fast.
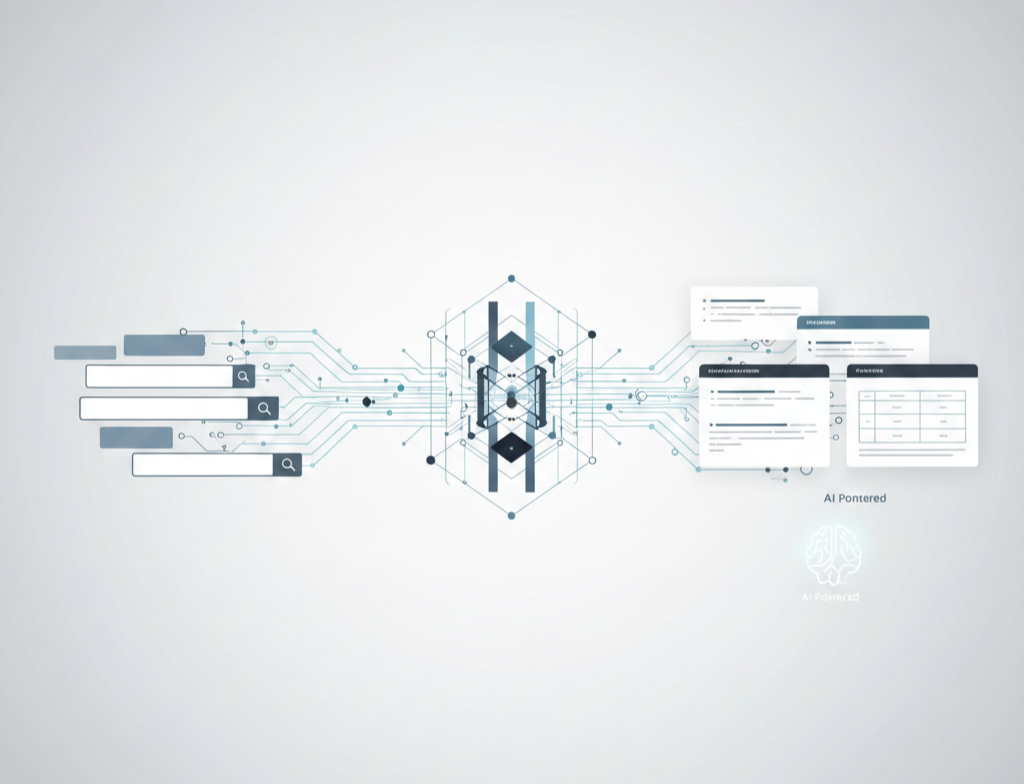
Google, Bing, and other platforms are no longer just “search engines.” They are answer engines powered by generative AI. Users are getting synthesized responses directly on results pages, inside chat interfaces, and across AI assistants — often without clicking a single website.
This guide will not promise shortcuts or overnight wins.
It will explain what Generative Engine Optimization (GEO) actually is, why it matters, and how businesses can adapt SEO strategy for AI-driven search environments — without burning budgets or chasing hype.
By the end, you should have clarity on:
-
What GEO really means (and what it doesn’t)
-
How generative AI selects, synthesizes, and cites content
-
Practical GEO strategies aligned with SEO fundamentals
-
Tools and services businesses commonly use to support GEO efforts
-
Where GEO is heading next — and what to prepare for now
What Is Generative Engine Optimization?
Defining Generative Engine Optimization (GEO):
Generative Engine Optimization (GEO) is the practice of optimizing content, structure, and brand signals so that generative AI systems can accurately understand, trust, and reference your information when generating answers.
Unlike traditional SEO — which primarily targets rankings on search engine results pages — GEO focuses on visibility inside AI-generated outputs.
This includes:
- Google’s AI Overviews and Search Generative Experience (SGE)
- Bing Copilot results
- AI assistants trained on web-scale data
- Enterprise AI search systems
In practical terms, GEO asks a different question:
“Will an AI system choose my content when explaining this topic?”
What Is Generative AI?
Generative AI refers to machine learning models that generate new content — text, images, code, or summaries — based on patterns learned from large datasets.
According to platform documentation from OpenAI, Google, and Microsoft, these systems:
- Do not “search” the web like humans
- Predict the most contextually relevant next words
- Rely heavily on structured, authoritative, and consistent information
This matters because AI does not reward keyword repetition — it rewards clarity, relevance, and reliability.
How Generative AI Works (Simplified for Marketers)
At a high level, generative AI systems:
- Interpret the user’s intent
- Identify authoritative sources or patterns
- Synthesize information into a single response
- Reduce redundancy and low-confidence signals
According to Google’s Search documentation, content that is:
- Well-structured
- Demonstrates expertise
- Clearly answers specific questions
is more likely to influence AI-generated summaries.
How Generative Engine Optimization Works in Practice
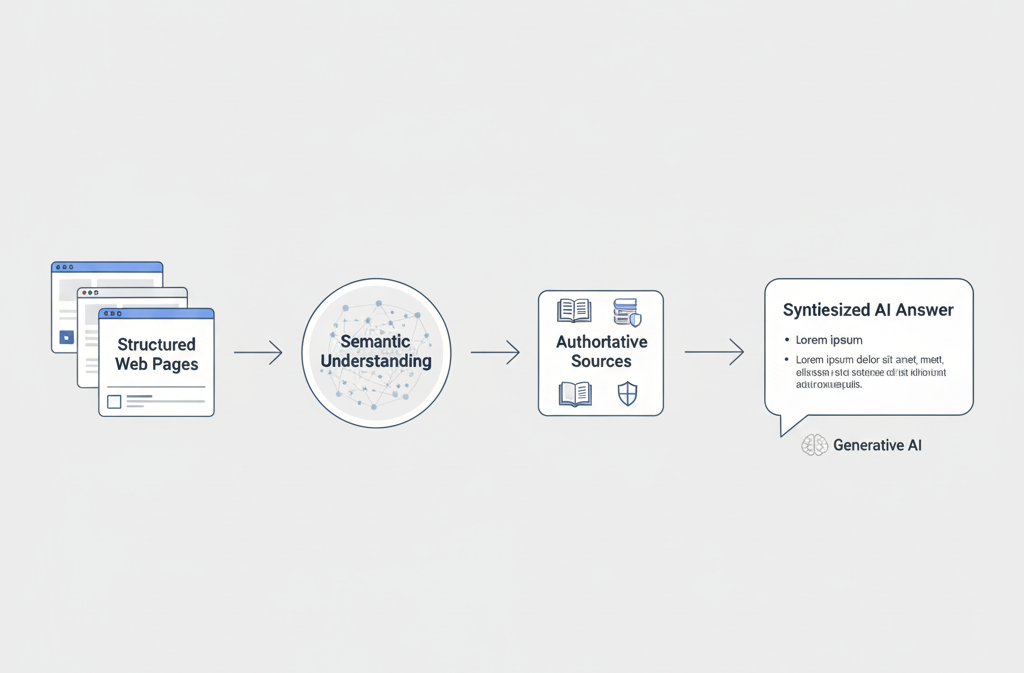
GEO does not replace SEO. It builds on it.
In real-world campaigns, GEO typically focuses on:
- Semantic clarity over keyword density
- Topical authority instead of isolated blog posts
- Explicit definitions and frameworks
- Clear authorship and credibility signals
- Machine-readable structure (headings, FAQs, schema)
Think of GEO as optimizing for interpretation, not just indexing. Read this detailed guide to learn more about generative engine optimization strategies.
Why GEO Matters for SEO & AI Search
The Shift from “Clicks” to “Answers”
Across multiple industries, analytics patterns show:
- Impressions rising
- CTR declining
- Brand mentions increasing without direct traffic
This is not SEO “failing.”
It’s SEO evolving.
According to Google Search guidelines, the goal is increasingly to:
“Provide the most helpful answer as efficiently as possible.”
If your content is not structured for AI interpretation, it may never be surfaced — even if it ranks.
GEO vs Traditional SEO: What’s the Difference?
| Area | Traditional SEO | Generative SEO / GEO |
|---|---|---|
| Primary Goal | Rank pages | Influence AI responses |
| Success Metric | Traffic, rankings | Visibility, citations, trust |
| Content Style | Keyword-optimized | Explanation-driven |
| Structure | Page-level | Topic-level |
| Attribution | URLs | Sources & entities |
In practice, businesses struggle most when they treat GEO as a separate tactic rather than a strategic layer on top of SEO.
Why Businesses Can’t Ignore GEO Anymore
Based on observed performance patterns:
- AI answers often reduce the need for multiple searches
- Brands cited in AI responses gain perceived authority
- Decision-makers trust synthesized explanations
GEO matters because:
- Visibility now happens before the click
- Authority is built at the explanation layer
- Early adopters shape AI knowledge graphs
Ignoring GEO doesn’t just risk traffic — it risks relevance.
Core Principles of Generative Engine Optimization
1. Topical Authority Beats Page Authority
According to industry-wide SEO consensus:
- AI systems prefer clusters over standalone pages
- Repetition across multiple credible pages reinforces trust
- One “ultimate” guide is not enough
- Supporting content must reinforce the same concepts consistently
This is why pillar–cluster content models align naturally with GEO.
2. Explicit Answers Outperform Clever Writing
AI systems do not appreciate creativity the way humans do.
They prioritize:
- Clear definitions
- Direct answers
- Logical progression
For example:
- “Generative Engine Optimization is…” performs better than metaphor-driven intros
- Step-by-step explanations outperform opinion-heavy content
Clarity is not boring — it is machine-friendly authority.
3. Experience Signals Matter More Than Claims
According to Google’s E-E-A-T framework:
- Demonstrated experience increases trustworthiness
- Authorship and credentials matter
GEO-friendly content includes:
- Explicit experience markers (“In real client campaigns…”)
- Clear author identification
- Review attribution when applicable
This isn’t branding — it’s context validation.
4. Neutral, Educational Tone Wins AI Trust
AI systems penalize:
- Over-promotional language
- Absolute claims
- Hype-driven framing
Platform guidelines consistently recommend:
- Neutral explanations
- Balanced perspectives
- Context-aware advice
This is why educational sections must stand alone without selling.
How To Start With GEO (Beginner-Friendly Guide)
Step 1: Audit Content for AI Readability
Start by reviewing existing content:
- Are definitions explicit?
- Are headings answering real questions?
- Is the language neutral and factual?
Common issues observed:
- Vague intros
- Mixed topics on one page
- Missing author context
Step 2: Build Topic Clusters, Not Isolated Posts
Instead of:
- “10 AI tools”
- “SEO tips 2024”
Shift toward:
- Pillar pages explaining core concepts
- MOFU blogs deep-diving into subtopics
- This reinforces topical authority — a key GEO signal.
Step 3: Structure Content for Interpretation
Use:
- Clear H2/H3 hierarchy
- Short paragraphs
- Lists where appropriate
- FAQ-style sections
According to Google Search documentation, structured content improves understanding for both crawlers and AI systems.
Step 4: Strengthen Entity & Credibility Signals
Include:
- Author name and credentials
- Consistent terminology
- Accurate references to platforms (Google, Meta, GA4)
Avoid:
- Anonymous content
- Unsupported claims
- Contradictory explanations
Overview of Tools & Services Supporting GEO
GEO is not about buying a single tool. It’s about using the right stack.
Common Tool Categories Used in GEO
1.SEO & Content Research Platforms
- Topic modeling
- Semantic keyword mapping
- SERP analysis
2.Content Optimization Tools
- Structure analysis
- Readability scoring
- Entity coverage
- GA4 behavior analysis
- Search Console impression tracking
- AI visibility monitoring (emerging)
👉 Check out the top tools and platforms for GEO
Services Businesses Often Use for GEO Execution
In practice, businesses use external support for:
- Content strategy architecture
- Pillar–cluster planning
- Technical SEO alignment
- AI-focused content audits
👉 Explore business use cases and services
Future Trends in Generative Engine Optimization
Trend 1: AI-Citation Optimization
As AI systems improve attribution, content that:
- Clearly defines concepts
- Uses consistent language
- Demonstrates expertise
will be more frequently cited.
Trend 2: Entity-Based SEO Becomes Standard
Search engines are moving from keywords to entities:
- People
- Brands
- Concepts
- GEO-ready content strengthens entity relationships rather than chasing rankings.
Trend 3: Fewer Clicks, Higher Authority
Traffic volume may decline for some queries — but:
- Brand trust increases
- Conversion quality improves
- Sales cycles shorten
- This requires a mindset shift from traffic obsession to influence optimization.
👉 Learn advanced GEO strategies for AI visibility
Final Thoughts: GEO Is Not a Shortcut — It’s a Discipline
Generative Engine Optimization is not about gaming AI systems.
It is about:
- Teaching machines clearly
- Structuring knowledge responsibly
- Building long-term authority
- Businesses that win in AI-driven search environments:
- Invest in clarity, not tricks
- Focus on sustainable knowledge assets
- Align SEO with how modern search actually works
Some organizations choose to work with agencies like Marketing Scrappers for execution support — especially when scaling GEO strategies across content, SEO, and technical infrastructure.
But regardless of who executes, the principle remains the same:
The future of SEO belongs to those who help AI understand — not those who shout the loudest.