
GEO Site Architecture For AI Answers & Searches
TL;DR:
GEO site architecture refers to designing your site so that generative engines (Google AI Overviews, Gemini, ChatGPT-style agents, Perplexity, etc.) can find, understand, and cite your content — through clear content clusters, schema and knowledge-graph signals, canonical/version control, and measurable experiments.
This guide gives you:
-
Step-by-step blueprint
-
Example sitemaps (SaaS / ecommerce / publisher)
-
Testing recipes
-
Competitor gaps
-
Schema snippets
Why GEO Site Architecture Matters
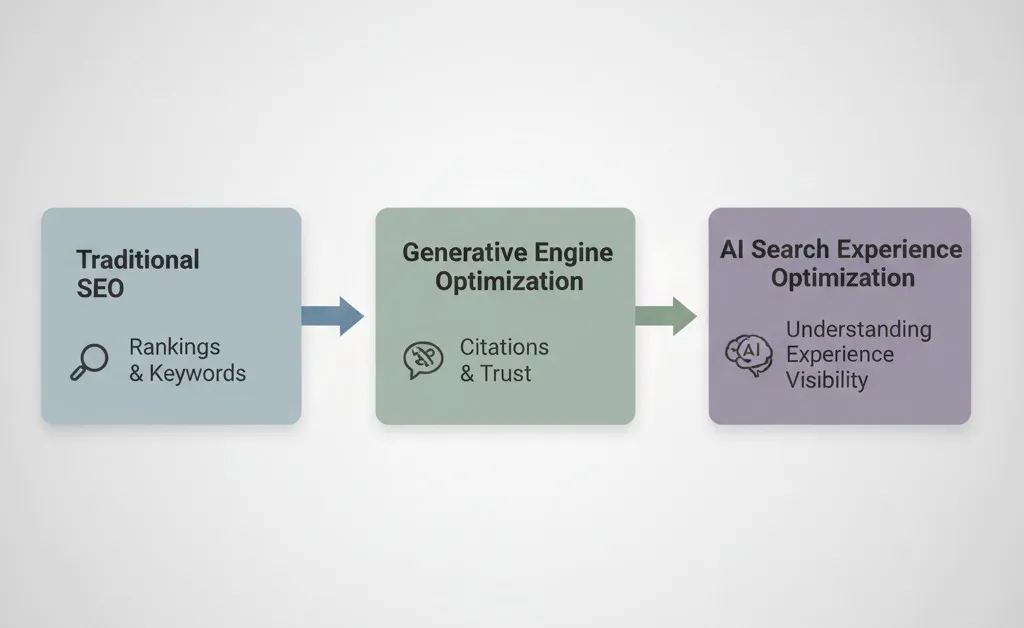
Generative Engine Optimization (GEO) is already the practical sibling of SEO: it’s about getting your brand and pages surfaced inside AI-generated answers, not just organic rankings. If AI answer boxes summarize the web, your site architecture decides if the model sees you as the canonical source.
AI Overviews and RAG systems are citation machines. If your structure is ambiguous, they’ll use someone else.
What This Guide Gives You
-
✅ Actionable architecture rules for GEO (pillar → cluster → snippet mapping)
-
✅ Granularity guide: what to keep short vs long for AI snippet use
-
✅ Internal-linking & entity clustering tactics for LLMs
-
✅ Canonical/versioning strategy so AIs cite the right source
-
✅ Example sitemaps (SaaS, ecommerce, publisher) in text diagrams
-
✅ Validation & measurement: how to test what AIs cite
-
✅ Competitor teardown: what Semrush, Backlinko, and others miss
-
✅ Lead magnet idea: downloadable GEO Audit Checklist (25 points)
GEO Site Architecture Best Practices
1. Map Pillar / Cluster Design to AI Intents
Generative engines treat queries as intents:
-
Direct Answer
-
How-to
-
Comparison
-
Example
Design your architecture so each intent has a predictable location:
Pillar page (authority)
-
Long-form canonical content (~2,000+ words, data, citations)
-
Acts as the “source node” in your content graph
-
Include: TL;DR (40–60 words), detailed body, and FAQs
Cluster pages (intent-specific)
-
How-tos, comparisons, short guides (300–800 words)
-
Link clearly back to the pillar with descriptive anchor text
Answer/FAQ blocks
-
Use short (40–60-word) blocks labeled like “Quick answer.”
-
Place them at the top of both pillar and cluster pages
-
Optimize for both snippet capture and RAG chunking
📌 Tip: Use H2/H3 formatting and semantic labels (e.g., “Quick Comparison”) — retrieval systems love it.
2. Content Granularity Rules: Short vs Long (Practical)
| Length | Use For |
|---|---|
| 40–60 words | Definitions, answers, snippet-friendly summaries |
| 300–900 words | Tactical how-tos, product FAQs, comparison pages |
| 1,500+ words | Pillars, studies, authoritative topical coverage |
Put the short answer at the top. Label it clearly. Use schema like
FAQPage,HowTo, ormainEntity.
3. Internal Linking & Entity Clustering for LLMs
LLMs prefer semantically structured internal links and clearly clustered content:
-
Explicit Entities: Use consistent names and define them via structured data.
-
Anchor text: Use intent-specific language (e.g., “Compare SaaS pricing plans” instead of “click here”).
-
Linking model:
-
Product → Use Cases → Case Studies → Docs
-
Topic Pillar → Subtopics → FAQs → Author Page
-
Model your structure like a graph, not just a tree. This mirrors how retrieval systems operate.
4. Canonicalization & Content Versioning Strategy
AI answers can cite outdated or duplicate content if your architecture is unclear.
✅ Set rel=canonical tags on all primary pages
✅ Add mainEntityOfPage, datePublished, dateModified in JSON-LD
✅ Display “Last reviewed” dates visibly for humans and machines
✅ Redirect outdated or test URLs to canonical pages
✅ Noindex test pages post-experiment
Bonus: Claim your Knowledge Panel (via Search Console or structured data) for strong entity authority.
5. Example Sitemaps (Visual Blueprints)
SaaS (B2B)
Ecommerce
Publisher
Testing & Validation: Which Pages Do AIs Actually Use?
You need proof — not guesses.
Quick Validation Recipe
-
Google Search Console
-
Find rising impressions on Q&A-style queries
-
Filter by AI Features if available
-
-
Manual Prompts
-
Run prompts in incognito on Perplexity / Gemini / Google AI
-
Record which URLs are cited
-
-
A/B Content Experiments
-
Two pages, one with answer block + schema, one without
-
Track inclusion via AI Overviews or prompt response
-
-
Watermarking
-
Insert a unique phrase like “TrendCue Insight: 2025-GEO” in answer blocks
-
Watch for that exact phrase in AI outputs
-
Tools, Schema & Knowledge Graph Starters
Key Structured Data Types
-
FAQPage,HowTo,Article,Product,Organization,Person -
Use Google’s Rich Results Test to validate
Build a Lightweight Knowledge Graph
-
Use Schema.org vocabulary
-
Track entities and relationships in a spreadsheet or simple JSON-LD
-
Migrate to a graph DB (optional) when scaling
Monitoring Tools
-
Google Search Console (Search Appearance filters)
-
SE Ranking / AWR / Semrush (AI Overview visibility reports)
-
Manual prompt testing framework (track citations per query)
✅ 25-Point GEO Audit Checklist
Here is a downloadable GEO Site architecture audit checklist, which includes:
-
Entity Home page created?
-
Short answer at top? (40–60 words)
-
JSON-LD types used?
-
Canonical tag in place?
-
dateModified + datePublished present?
-
Is there an FAQ schema?
-
Are cluster pages one click from the pillar?
-
Does internal linking reflect semantic relationships?
-
Was prompt testing performed?
-
Is a unique watermark phrase used?
-
…(15+ more)
🟢 Want this checklist now? Click here to Check Now…
Conclusion
GEO Site architecture = traditional SEO structure + answer blocks + entity signals + version control + experimentation.
Build clear pillars, give crisp answers, mark up your content for machines, and test like a scientist.
Do that — and your brand won’t just rank. It becomes the source AI quotes.
FAQ (People-Asked GEO Questions)
What is GEO vs SEO?
GEO optimizes for generative AI answers and attribution; SEO optimizes for classic SERPs. They overlap, but GEO favors structured, answerable content.
How long should an AI snippet be?
40–60 words. Bullet lists and labeled “Quick Answer” sections work best.
How do I test if AI used my content?
Use:
-
Manual prompts
-
Google Search Console
-
Watermarking
-
A/B schema experiments
Does schema guarantee AI inclusion?
No, but it helps engines parse structure. Combine it with fresh content, authority, and clear answers.
Should I split short vs long content?
No — combine: TL;DR at top, detailed guide below.
Further Reading & Sources
-
What is Generative Engine Optimization — Search Engine Land
-
Google: AI features and your website — Google for Developers
-
How to build a content knowledge graph — Schema App / FalkorDB
-
Canonicalization guide — Google Search Central
-
GraphRAG Retrieval — Neo4j, Snowflake, GraphDBs





1 Comment
Thank you for your sharing. I am worried that I lack creative ideas. It is your article that makes me full of hope. Thank you. But, I have a question, can you help me?